BioRice
Decarbonizing Rice at Scale
Decarbonizing Rice at Scale
Microbes
Applying Microbes to mediate Methane
Farmers
Automated Delivery Mechanism to
reach and incentivize farmers
reach and incentivize farmers
Climate
Mitigating the most urgent greenhouse gas
Acting Rapidly to Mitigate Methane
Methane mitigation is essential for addressing climate change.
Pursuing all methane mitigation measures now could slow near-term warming by 30 percent, avoid 0.25°C of additional warming, and set us on a path to avoid more than 0.5°C warming by end of century.
Global methane comes from rice cultivation
12%
Close to the emissions from fuel burnt by the entire shipping industry
Number of times methane is more potent than CO2
84x
Cutting methane is the single fastest, most effective opportunity to immediately slow down the rate of warming
Millions of farmers worldwide
150
90% of the world’s rice is cultivated in Asia by smallholder farmers
Global methane comes from rice cultivation
12%
Close to the emissions from fuel burnt by the entire shipping industry
Number of times methane is more potent than CO2
84x
Cutting methane is the single fastest, most effective opportunity to immediately slow down the rate of warming
Number of farmers worldwide
150
90% of the world’s rice is cultivated in Asia by smallholder farmers

Harnessing Microbes to Decarbonize Rice
Amplifying Bio-based Solutions for the Mitigation of Methane Emissions
BioRice harnesses bio-based microbes as ecosystem engineers to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and increase yield.
By changing the soil chemistry, microbes increase beneficial sulfates in the soil and keep that level stable — no sulfate supplementation needed. Microbes do not directly harm methane producers but they create conditions that crowd them out.
The result is significantly less methane emission from rice cultivation.
Rewarding farmers for addressing climate change
Access to carbon credits could be a tipping point to incentivize farmers to switch to lower-GHG emitting practices – contributing to emissions reduction on a global scale
For Farmers
Access to high-integrity carbon credits | Earn income by switching to sustainable practices | New revenue stream from selling carbon credits | Ease of access to carbon markets | Direct, fair share of carbon credit cash via mobile wallet
For Governments
Uplift livelihoods of millions of farming families | Enhance food security as population and demand for rice increase | Access to high-value carbon credits under Article 6 of the Paris Agreement | Action towards The Globe Methane Pledge
For Companies
Access to sustainable agriculture carbon credits to reach net-zero goals | Tangible contribution to the future of sustainable foods | Positive impact on poverty alleviation
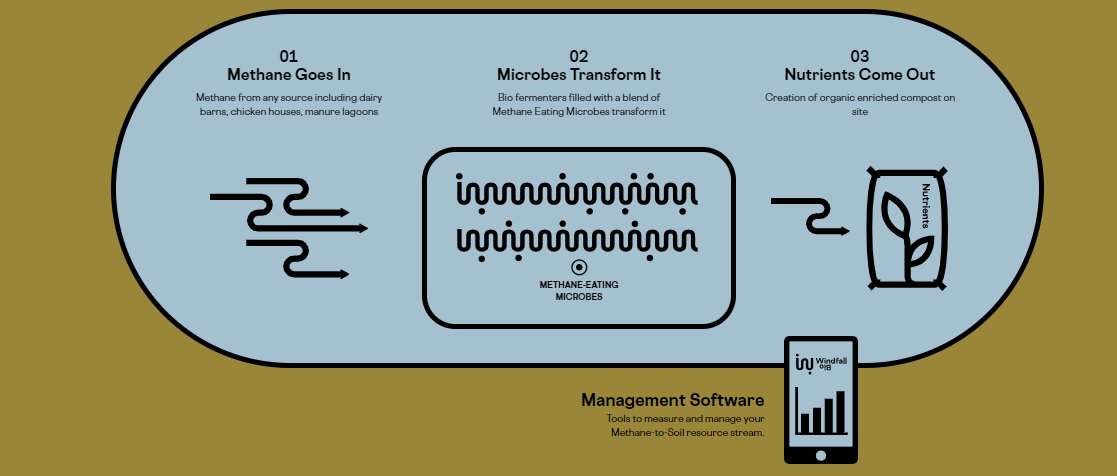
WITH WINDFALL BIO
Methane = A Resource Waste
Methane is a dynamic resource, only becoming a greenhouse gas when it’s not harnessed for something useful. Our nature-based technology enables farmers to transform methane from their operations into rich, organic soil nutrients right on site.
How It Works